
RYB vs RGB vs CMYK Color Models: Everything You Need To Know!
Colors are such an important part of our lives! This is especially true if you are an artist, graphic designer, or in any type of business, printing, advertising, or marketing field. Colors aren’t just visually pleasing but they also have the power to communicate ideas and evoke certain emotions and this is why it is so important to understand how colors work and how to use them.
In this article, we are going to dive into the very interesting world of the RYB, RGB, and CMYK color models to understand the different ways that colors are represented and used in design, printing, and art.
Let’s Begin!
What Is A Color Model?
A color model is a system that helps us to describe, represent and organize colors in a structured way by using numbers.
Using a color model gives artists and designers an easy way to understand how colors can be created and displayed allowing them to effectively work with color in their art and designs. Color models also help us to communicate and reproduce colors accurately making them an indispensable tool that is essential for artists, designers, or anyone else who works with color.
Additive and Subtractive Color Models
Before we begin exploring RYB, RGB, and CMYB color models it is important to understand two different color models known as Additive and Subtractive Color Models. These models help us to understand how colors are created and mixed.
Additive Color Models
The additive color model uses light to create colors and it is used in light-emitting devices such as computer screens, mobile devices, televisions, and projectors. An enormous range of colors can be created by combining different intensities of light.
In the additive model, we start with a black background and as we add different colors of light they combine to create new colors.
There are three primary colors of light: Red, Green, and Blue (also known as RGB).
When we combine red light, green light, and blue light together in varying amounts different colors are created. And if we combine them at their full intensities, we get pure white light!
Key Points: The Additive Model starts with a black background and adds red, green, and blue light to create different colors. Used in on-screen displays.
Subtractive Color Models
The subtractive color model is used in traditional art and printing where colors are used on paper or canvas.
In this model, we use different pigments such as paints and inks that absorb or subtract certain colors of light to create new colors. In this color model, we start with a white background and as we mix pigments together they create new colors.
The primary colors in the subtractive model are Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, and Black (CMYK).
By combining different amounts of these colors we can create a wide range of colors to use in the printing process and painting. And ultimately, if we combine all the colors in the subtractive model we will end up with black.
Key Points: The Subtractive Model starts with a white background and pigments are used that absorb or subtract specific colors of light to create new colors. Used in printing and art.
The RGB Color Model
The RGB color model is an Additive Color Model meaning that different colors of light are added to a black background to create new colors.
How the RGB Model Is Represented
In the RGB color model, each primary color is assigned a value ranging from 0 to 255. These numbers represent the intensity level of each color with 0 meaning no intensity and 255 meaning full intensity.
By combining these three primary colors at different intensity levels we can create millions of different colors that can be used on websites or in our designs and branding.
RGB values are displayed in the following format: RGB(RR,GG,BB).
RGB Primary Colors
The primary colors in the RGB color model are Red, Green, and Blue and in the world of digital art and design, these are the primary colors used to create all the colors you need for your designs.
This is what the three primary colors look like along with their RGB values and hex codes:
Red
#FF0000
RGB(255,0,0)
Green
#00FF00
RGB(0,255,0)
Blue
#0000FF
RGB (0,0,255)
As you can see in the red RGB example above, the red value is set to 255 which is at full intensity whereas the green and blue values are set at zero. Likewise the same can be seen in the green and blue color examples as well.
Related: Primary Colors: A Guide to the Foundation Of Color Theory
RGB Secondary Colors
In the RGB color model, you create secondary colors by combining the primary colors of Red, Green, and Blue.
The secondary colors in the RGB color model are:
- Cyan: Cyan is created by mixing green and blue light and it contains no red light.
- Magenta: Magenta is produced by combining red and blue light but it contains no green light.
- Yellow: Yellow is created by mixing red and green light with no blue light added.
Cyan
#00FFFF
RGB(0,255,255)
Magenta
#FF00FF
RGB(255,0,255)
Yellow
#FFFF00
RGB (255,255,0)
Related: Secondary Colors: Everything You Need To Know!
Visual Representation Of The RGB Color Model
Sometimes it is a lot easier to understand how something works when you can see it! This is what the RGB color model looks like with its primary and secondary colors. Note how if all the colors are mixed together you end up with pure white.
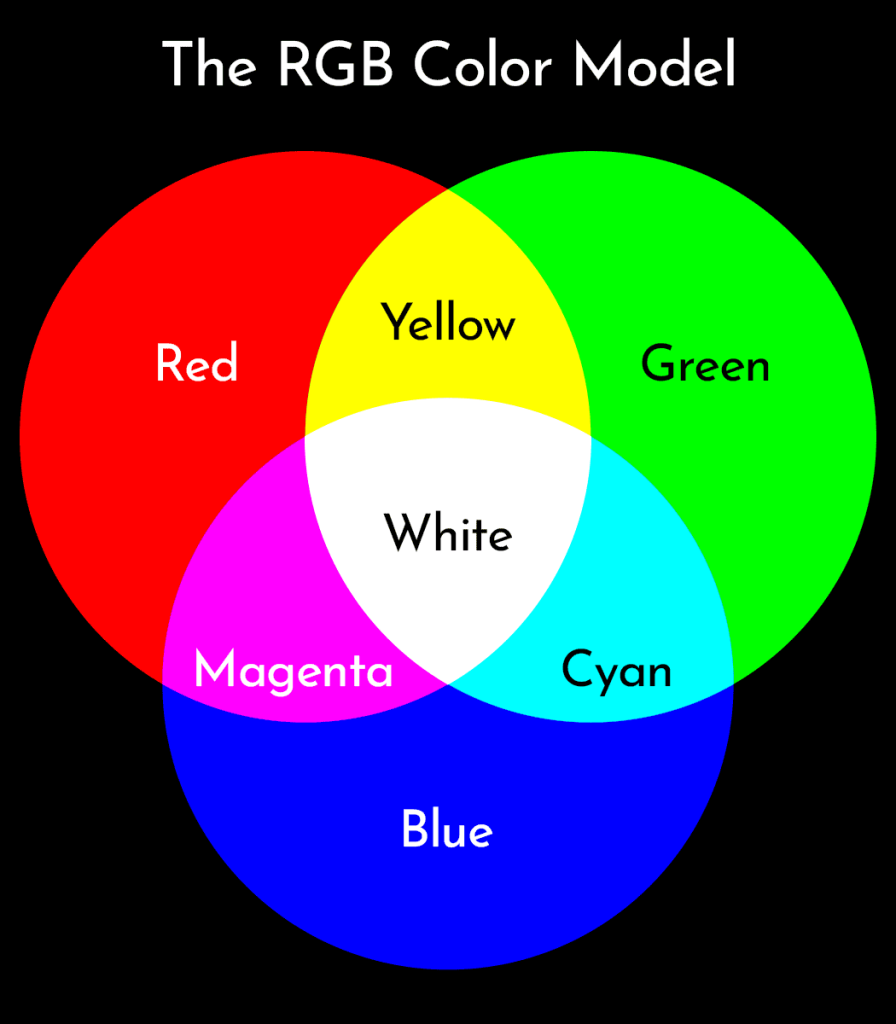
When To Use The RGB Color Model
The RGB color model is used to display color in any digital medium. Here are a few of the common places where RGB is used:
- Web Design and Digital Media: The RGB color model is used when creating or displaying visuals on digital marketing platforms such as websites, computer screens, and, mobile applications.
- Photography and videography: RGB is used for accurately capturing, editing, and displaying color in images, videos, and other digital devices.
- Graphic Design: RGB is also used to specify the colors used when creating graphics for digital marketing materials such as logos, online adverts, infographics, branding materials, social media posts, and online photos.
Key Points: The RGB color model is used when colors are displayed on any on-screen medium.
The CMYK Color Model
The CMKY color model is a Subtractive Color Model meaning that colors are created by starting with a white background and adding layers of ink or pigment to subtract or absorb light. CMYK plays a vital role in the world of printing and art and is crucial to achieving accurate and vivid results on paper.
CMYK represents the colors Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, And Black.
What Is The CMYK Color Codes Format?
In the CMYK color model, percentages are used to specify how much of each color should be used.
CMYK Color Codes Are Displayed In the following Format: CMYK(C%, M%, Y%, K%)
The CMYK color code specifies what percentage of cyan, magenta, yellow and black should be used with each value ranging from 0% to 100%.
For example, if you wanted to create white, the CMYK color code is CMYK(0%, 0%, 0%, 0%) which shows us that no ink is used.
On the other hand, CMYK(100%, 100%, 100%, 100%) represents a solid black color where all four inks are used at their full intensity.
CMYK Primary Colors
Cyan, Magenta, and Yellow are the primary colors used in the CMYK color model. Along with black, this is what they look like:
Cyan
#00FFFF
RGB(0,255,255)
Magenta
#FF00FF
RGB(255,0,255)
Yellow
#FFFF00
RGB (255,255,0)
Black
#000000
RGB (0,0,0)
CMYK Secondary Colors
In the CMYK model, secondary colors are created when you combine two of the CMYK primary colors in equal proportions.
The secondary colors in the CMYK color model are:
- Red: Created by combining magenta and yellow inks in equal proportions.
- Green: Created by combining cyan and yellow inks in equal proportions.
- Blue: Created by combining cyan and magenta inks in equal proportions.
This is what the secondary colors look like:
Red
#FF0000
RGB(255,0,0)
Green
#00FF00
RGB(0,255,0)
Blue
#0000FF
RGB (0,0,255)
Visual Representation Of The CMYK Color Model
Once again, let’s take a look at what the CMYK color model looks like visually. As you can see, black is created when you mix all the colors together.
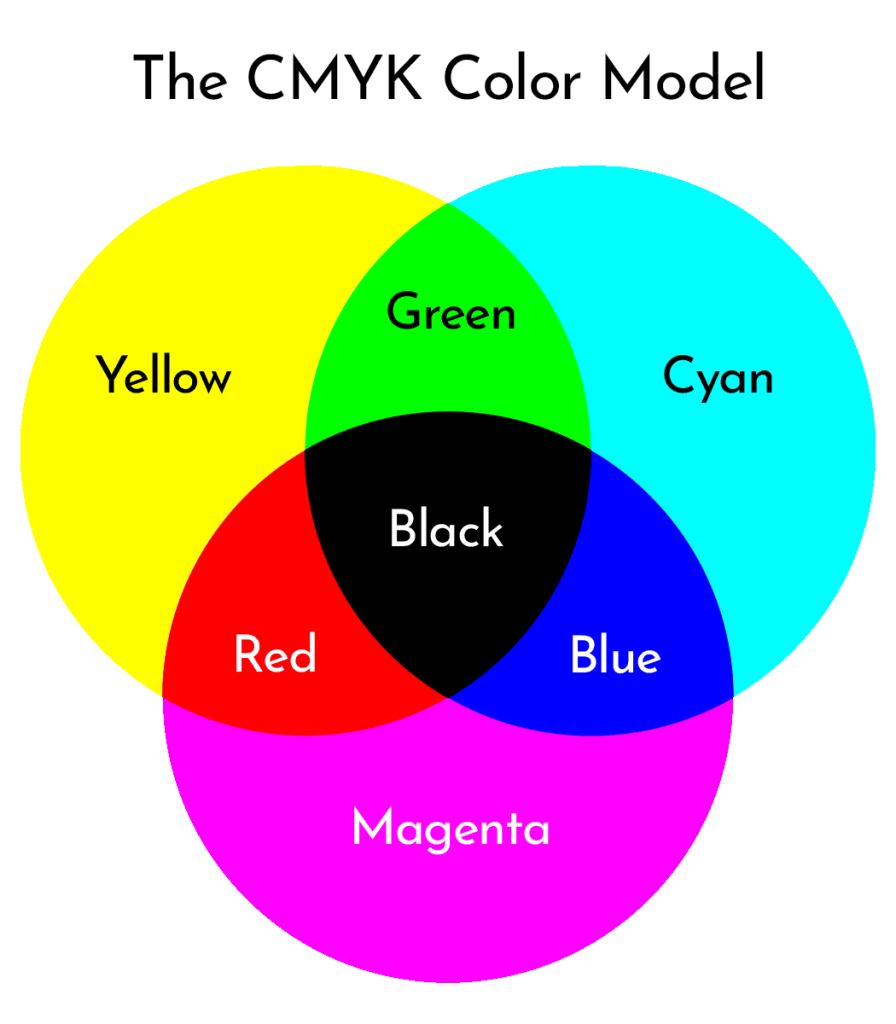
How Does The CMYK Color Model Work?
In the CMYK color model, colors are created by mixing and combining different percentages of the four ink colors.
During the printing process, the printer will use four ink color cartridges (cyan, magenta, yellow and black) applying specific combinations of each color at different intensities to create different colors on printed materials.
What Does The Letter “K” Stand For In CMYK?
In the CMYK color model, the letter “K” stands for “Key” and it represents black in the color model.
The letter “K” is used to avoid any confusion that might be caused by using the letter “B” which is used for “Blue” in the RGB color model.
Within the CMYK color model key, or black is used to give contrast and depth to an image.
When To Use The CMYK Color Model
The CMYK color model is used when you want to specify what colors should be used when physically printing something.
Here are some examples of where you would use the CMYK color model:
- Print and Publishing: CMYK is the go-to color model for the printing industry where the colors for magazines, brochures, flyers, packaging, and other printed materials need to be accurately printed.
- Advertising and Branding: Brochures, flyers, billboards, business cards, etc all rely on the CMYK color model to print to specify the colors that need to be printed.
- Promotional Merchandise: Things such as t-shirts, hats, mugs, and other promotional merchandise and clothing also use this color model.
Key Points: The CYMK color model is used when colors need to be physically printed.
The RYB Color Model
The RYB color model is not widely used in the digital art or printing industries but it is still a valuable tool for traditional artists who work with physical pigments such as paints, pastels, colored pencils, etc.
Just like the CMYK color model, the RYB color model is also considered to be a Subtractive Color Model.
RYB Primary Colors
You guessed it! The primary colors in the RYB color Model are Red, Yellow, and Blue!
Red
#FF0000
RGB(255,0,0)
Yellow
#FFFF00
RGB(0,255,0)
Blue
#0000FF
RGB (0,0,255)
Related: Primary Colors: A Guide to the Foundation Of Color Theory
RYB Secondary Colors
The RYB secondary colors are created when equal amounts of the primary colors are mixed together.
These are the colors that are created:
- Orange: Created by mixing red and yellow.
- Green: Created by mixing yellow and blue.
- Purple: Created by mixing blue and red.
This is what the RYB secondary colors look like:
Orange
#FF0000
RGB(255,165,0)
Green
#00FF00
RGB(0,255,0)
Purple
#800080
RGB (128,0,128)
Keep in mind that because the RYB color model is primarily used in traditional art it doesn’t have standardized codes associated with its colors and because of this, the colors can vary depending on how much of each primary color is used.
Visual Representation Of The RYB Color Model
Just like the previous two color models, the RYB color model has 3 primary colors and three secondary colors. This is what they look like:
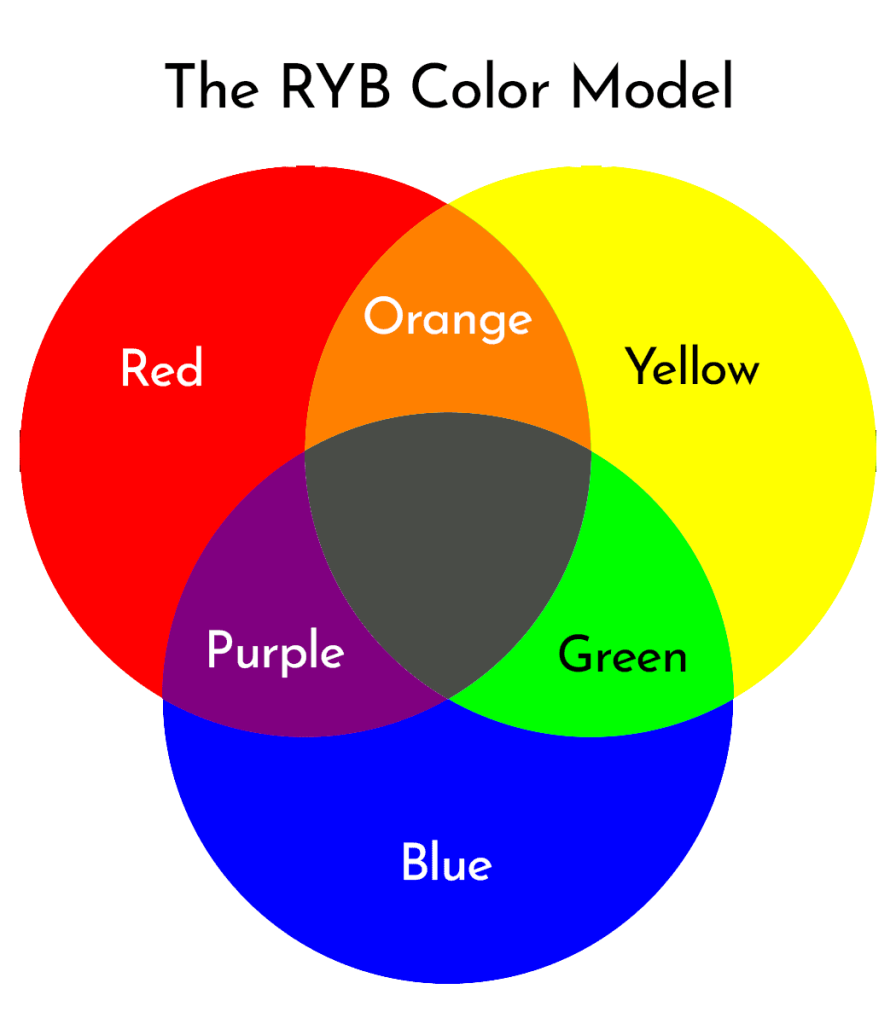
Key Points: The RYB color model is used in traditional art where pigments are used to create colors.
Frequently Asked Questions
It’s especially important to understand how the RGB and CMYK color models work when it comes to printing colors VS on-screen display colors.
Here are a few of the most common questions people have when using them:
When To Use RGB VS CMYK?
Use the RGB model when your designs are going to be displayed digitally – website design, social media graphics, multimedia presentations, video, etc.
Use the CMYK color model when your designs are going to be printed – brochures, flyers, business cards, magazines, etc.
Do I Need To Convert RGB to CMYK For Printing?
If you are planning to have your images and designs professionally printed, then it is a good idea to convert your RGB images to the CMYK color model. By converting RGB to CMYK you ensure that the color in your image will be accurate when printed.
The best advice I can give is to speak to your printer and follow their guidelines so that the best print quality is achieved.
What Happens If You Print RGB Instead Of CMYK?
If you print a RGB image without converting it to CMYK you could encounter some problems with the final result. This is because when an image is sent directly to a printer without converting it first, the printer will try to interpret the RGB color values and convert them to CMYK on the fly. This can result in the colors being less vibrant or inaccurate compared to what is seen on the screen. There may also be a loss of details and the brightness and contrast of the image may be affected.
Most professional design software such as Adobe Photoshop gives you the option to convert your images into the CMYK color mode easily.
Do Printers Automatically Convert RGB to CMYK?
Yes and no. If a file is not converted to CMYK before it is printed, the printer will do its best to convert the colors and make the adjustments for you which could result in colors that don’t look as they should.
If you are printing from your own computer at home or in your office you might not care too much about what the printed colors look like in which case you can allow your printer to make the color adjustments for you.
However, if you are having your work professionally printed at a commercial printer you will want to make sure that the colors that are printed are just as good on paper as what they look on screen.
Remember that getting the colors wrong can be a VERY costly mistake so if you aren’t sure about exactly what the printer needs then speak to them so that there is no confusion or misunderstanding. You can also ask your printer to give you a print proof so that you can see what the colors look like before committing to the print job.
Why Is RGB Not Suitable For Printing?
The RGB color model is not suitable for printing because RGB has a wider color range than the CMYK color model and many of the colors are highly saturated and very vibrant.
Unfortunately, this means that these colors can’t be reproduced exactly when physically printing them which often results in the colors being dull or different from what you expected.
RGB Screen Colors VS CYMK Print Colors
To give you an idea of how colors may change when you see them on screen VS when they are printed, this is what they could look like:
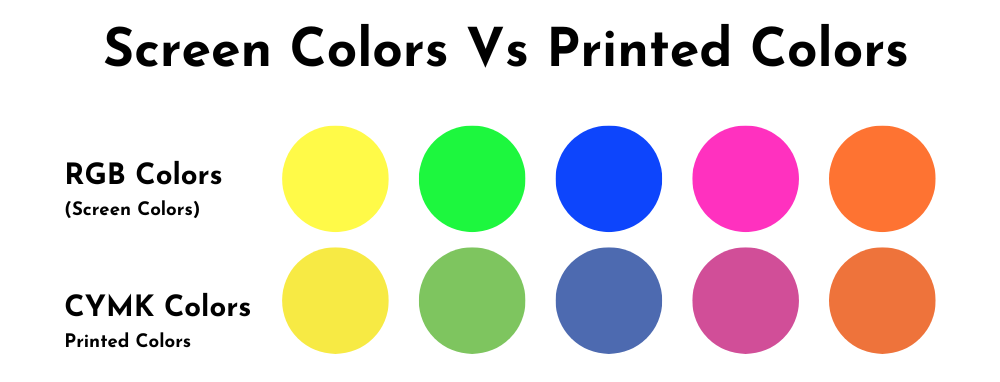
As you can see, the CYMK color could appear more muted and dull than their RGB counterparts.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between the RGB, RYB, and CMYK color models is essential especially if you are starting a small business and you are wanting to choose colors for your business’s color palette or website.
It’s especially important to keep the differences between the RGB VS CMYK color models in mind when it comes to printing. Just because a color looks good on screen doesn’t mean it will look the same when it is printed! So always check exactly what your color will look like when they are printed before committing to an expensive professional printing job!


